Introduction
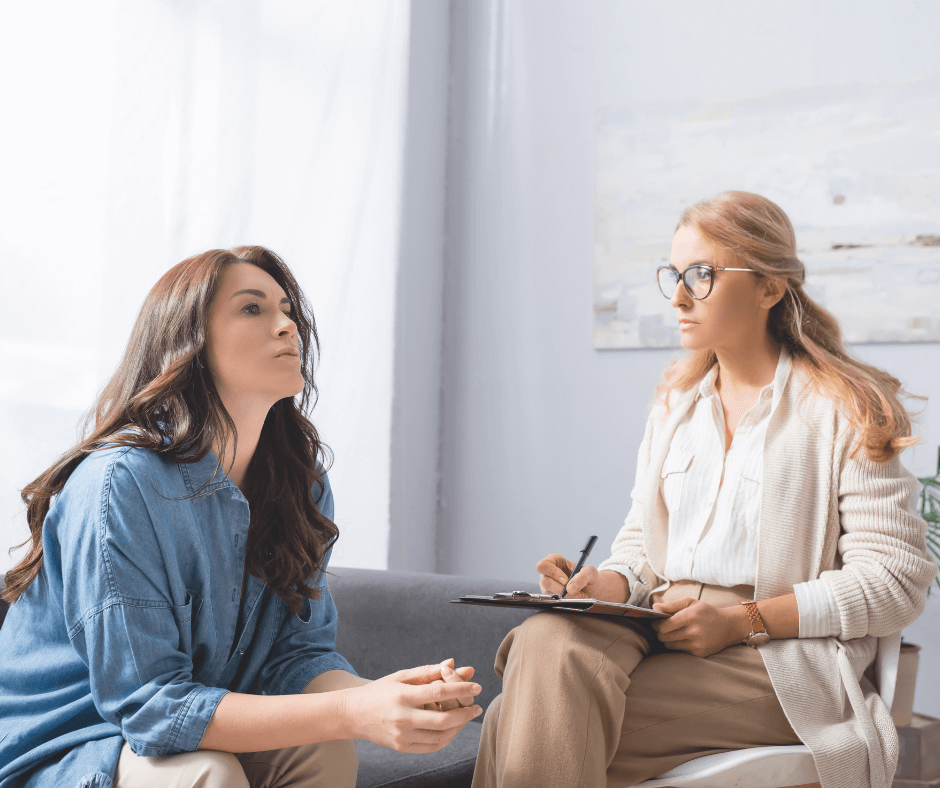
Depression is a complex and pervasive mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can manifest in various forms, impacting an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and daily functioning. While the causes of depression are multifaceted, ranging from genetic factors to life events, one crucial aspect of its management is therapy. In this article, we will explore the role of therapy in understanding and recovering from depression.
What is Depression?
Before delving into Therapy, it’s essential to grasp the nature of depression. Depression is not just fleeting sadness; it’s a prolonged state of low mood that interferes with daily life. Common symptoms include persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
Types of Therapy for Depression
Therapy, also known as counseling or psychotherapy, is a crucial component of depression treatment. Various therapeutic approaches have proven effective in helping individuals manage and overcome depression. Here are some common types:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used form of therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It helps individuals develop coping strategies and problem-solving skills.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): IPT centers on improving communication and relationship patterns. It’s particularly beneficial for those whose depression is linked to relationship difficulties or significant life changes.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: This type of therapy explores unconscious thoughts and emotions, often tracing them back to early experiences. Psychodynamic therapy aims to increase self-awareness and understanding.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Mindfulness practices, such as Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), involve cultivating awareness of the present moment. These techniques can be effective in preventing relapse for individuals with recurrent depression.
The Therapeutic Process
Engaging in therapy for depression is a collaborative process between the individual and the therapist. The therapeutic journey often involves the following steps:
- Assessment: In the initial sessions, therapists work to understand the individual’s history, symptoms, and life circumstances. This assessment helps tailor the therapeutic approach to the individual’s specific needs.
- Goal Setting: Together, the therapist and individual establish realistic and achievable goals for therapy. These goals may include symptom reduction, improved coping skills, and enhanced overall well-being.
- Exploration and Insight: Therapy provides a safe space for individuals to explore their thoughts and feelings. Through dialogue, individuals gain insights into the root causes of their depression and develop a deeper understanding of themselves.
- Skill Building: Therapists equip individuals with practical skills and coping mechanisms to navigate challenges and manage symptoms effectively. These skills may include stress management, communication strategies, and relaxation techniques.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular check-ins and assessments help monitor progress and adjust therapeutic strategies as needed. This ongoing feedback loop ensures that therapy remains tailored to the individual’s evolving needs.
Benefits of Therapy in Depression Recovery
Therapy offers numerous benefits in the journey towards depression recovery:
- Emotional Support: The therapeutic relationship provides a supportive and non-judgmental space where individuals can express their emotions openly.
- Skill Development: Individuals learn valuable skills to cope with stress, manage negative thoughts, and improve overall emotional well-being.
- Improved Relationships: Therapeutic interventions often result in better communication and interpersonal skills, positively impacting relationships with others.
- Increased Self-Awareness: Through self-reflection and exploration, individuals develop a deeper understanding of themselves, their triggers, and their strengths.
- Prevention of Relapse: Many therapeutic approaches, such as CBT and mindfulness-based therapies, are effective in preventing the recurrence of depressive episodes.
Conclusion
In the complex landscape of depression, therapy emerges as a beacon of hope. It provides a structured and supportive environment for individuals to understand, manage, and ultimately recover from depression. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to depressive symptoms, therapy empowers individuals with the tools they need to lead fulfilling and emotionally healthy lives. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, reaching out to a qualified mental health professional can be the first step toward healing and recovery.
Depression is a multifaceted mental health condition that affects millions worldwide, often impacting emotional well-being, physical health, and daily functioning. Therapy stands out as one of the most effective approaches for addressing depression, offering a safe and supportive environment where individuals can explore their thoughts, emotions, and experiences without judgment. Through guided conversations and evidence-based techniques, therapists help clients identify underlying factors that may be contributing to their symptoms, whether those stem from past trauma, ongoing stress, biological influences, or a combination of these elements. By understanding these root causes, individuals can learn practical coping strategies that not only alleviate symptoms but also build resilience for the future. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy, and other modalities each provide different frameworks for fostering emotional growth and recovery. In some cases, therapy may be complemented by medication prescribed by a qualified healthcare provider, particularly when symptoms are severe or persistent. This makes accurate information about treatments and their availability crucial, as patients often have questions about commonly discussed options, such as whether certain medications like Neurontin over the counter are accessible, and learning the correct facts can prevent misunderstandings. The therapeutic process also encourages the development of healthier lifestyle habits, including improved sleep routines, balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity, all of which play a role in mental health. Over time, therapy can help individuals regain a sense of purpose, improve their relationships, and increase their capacity to manage stress effectively. Importantly, progress in therapy is often gradual, requiring patience and consistent effort, but even small steps forward can significantly enhance quality of life. Support from friends and family can further strengthen the healing process, providing encouragement and reinforcing positive changes. As awareness of mental health grows, more people are recognizing the value of professional help and moving beyond the stigma that once surrounded therapy. Ultimately, seeking therapy for depression is not only about symptom relief but also about creating a sustainable foundation for long-term emotional well-being. Those who take the step to engage in therapy often find that the journey, while challenging at times, leads to profound personal growth and a renewed sense of hope for the future.